Majestic First Images from Rubin Observatory Show Universe in More Detail Than Ever Before
Astronomy fans can zoom in practically forever into the stunning first images from the Vera C. Rubin Observatory
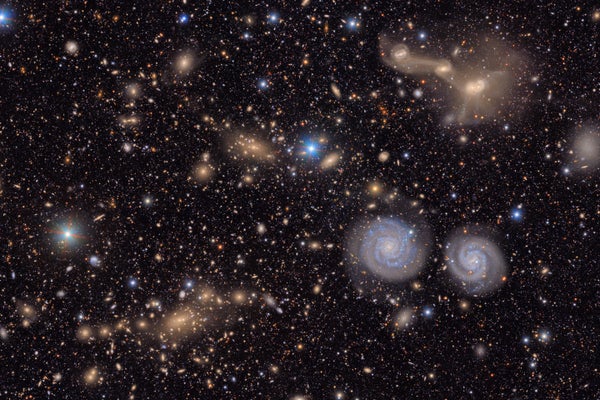

This image shows a small section of NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory’s total view of the Virgo cluster. Visible are two prominent spiral galaxies (lower right), three merging galaxies (upper right), several groups of distant galaxies, many stars in the Milky Way galaxy and more.
NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory
Editor’s Note (6/23/25): This story will be updated with additional images and details shortly after 11 A.M. EDT.
Welcome to a mind-blowing new era of astronomy.
The long-awaited Vera C. Rubin Observatory, a cutting-edge new telescope perched atop a mountain in Chile, is releasing its first images of the universe on June 23—and its views are just as jaw-dropping as scientists hoped. (The observatory is holding a celebratory event today at 11 A.M. EDT to reveal additional images that you can watch a livestream of on YouTube. In addition, organizations are hosting watch parties open to the public around the world.)
On supporting science journalism
If you’re enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
The new images come from only 10 hours of observations—an eyeblink compared with the telescope’s first real work, the groundbreaking, 10-year Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) project. On display are billowing gas clouds that are thousands of light-years away from our solar system and millions of sparkling galaxies—all emblematic of the cosmic riches that the observatory will ultimately reveal.
A brief excerpt from a longer video made from over 1,100 images captured by NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory. It begins with a close-up of a spiral galaxy then zooms out to reveal about 10 million galaxies. Those 10 million galaxies are roughly .05% of the approximately 20 billion galaxies Rubin Observatory will capture during its 10-year Legacy Survey of Space and Time.
Credit: NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory
“In a lot of ways, it almost doesn’t matter where we look,” said Aaron Roodman, a physicist at Stanford University and program lead for the Rubin Observatory’s LSST Camera, in a preview press conference held on June 9.
“We’re going to see changing objects; we’re going to see moving objects; we’re going to get a view of thousands and thousands of galaxies of stars in any field we look at,” he said. “In some sense, we could have looked anywhere and gotten fantastic images.”
In the end, the team decided to share several mosaics of images from the observatory that highlight its extremely wide field of view, which can capture multiple alluring targets in a single snapshot.
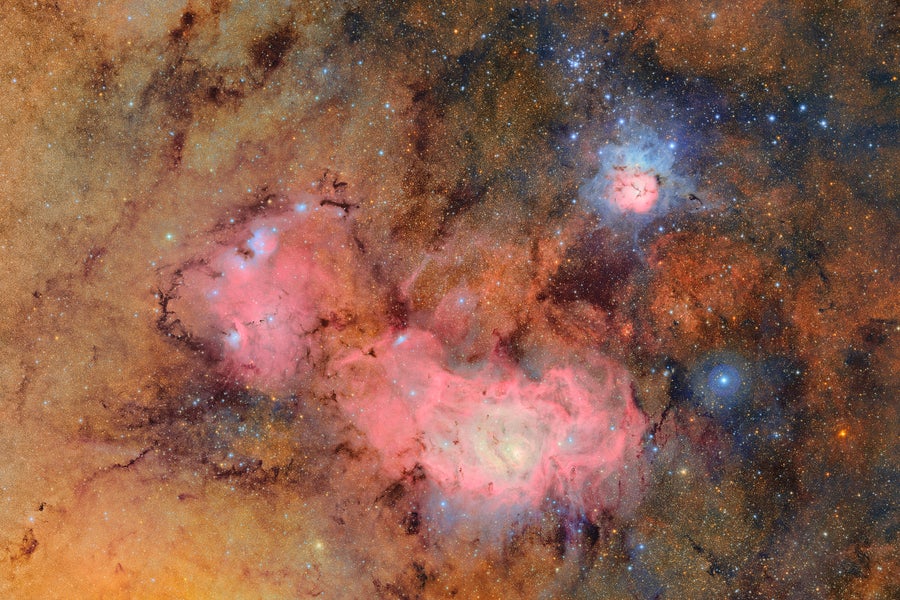
This image combines 678 separate images taken by NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory in just over seven hours of observing time. Combining many images in this way clearly reveals otherwise faint or invisible details, such as the clouds of gas and dust that comprise the Trifid nebula (top right) and the Lagoon nebula, which are several thousand light-years away from Earth.
NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory
The view above of the Triffid Nebula (top right) and Lagoon Nebula includes data from 678 individual images captured by the Rubin Observatory. Scientists stack and combine images in this way to see farther and fainter into the universe. The Triffid Nebula, also known as M20, and the Lagoon Nebula, also known as M8, are star-forming regions both located several thousand light-years away from Earth in the constellation Sagittarius.
The observatory also captured an initial view of the Virgo Cluster, a massive clump of galaxies located in the constellation of the same name. Individual detail images (at top and below) show a mix of bright Milky Way stars against a backdrop of myriad more distant galaxies. In addition, the team has released a teaser video of a stunning zoomable view of some 10 million galaxies that was created by combining some 1,100 images taken by the new observatory.
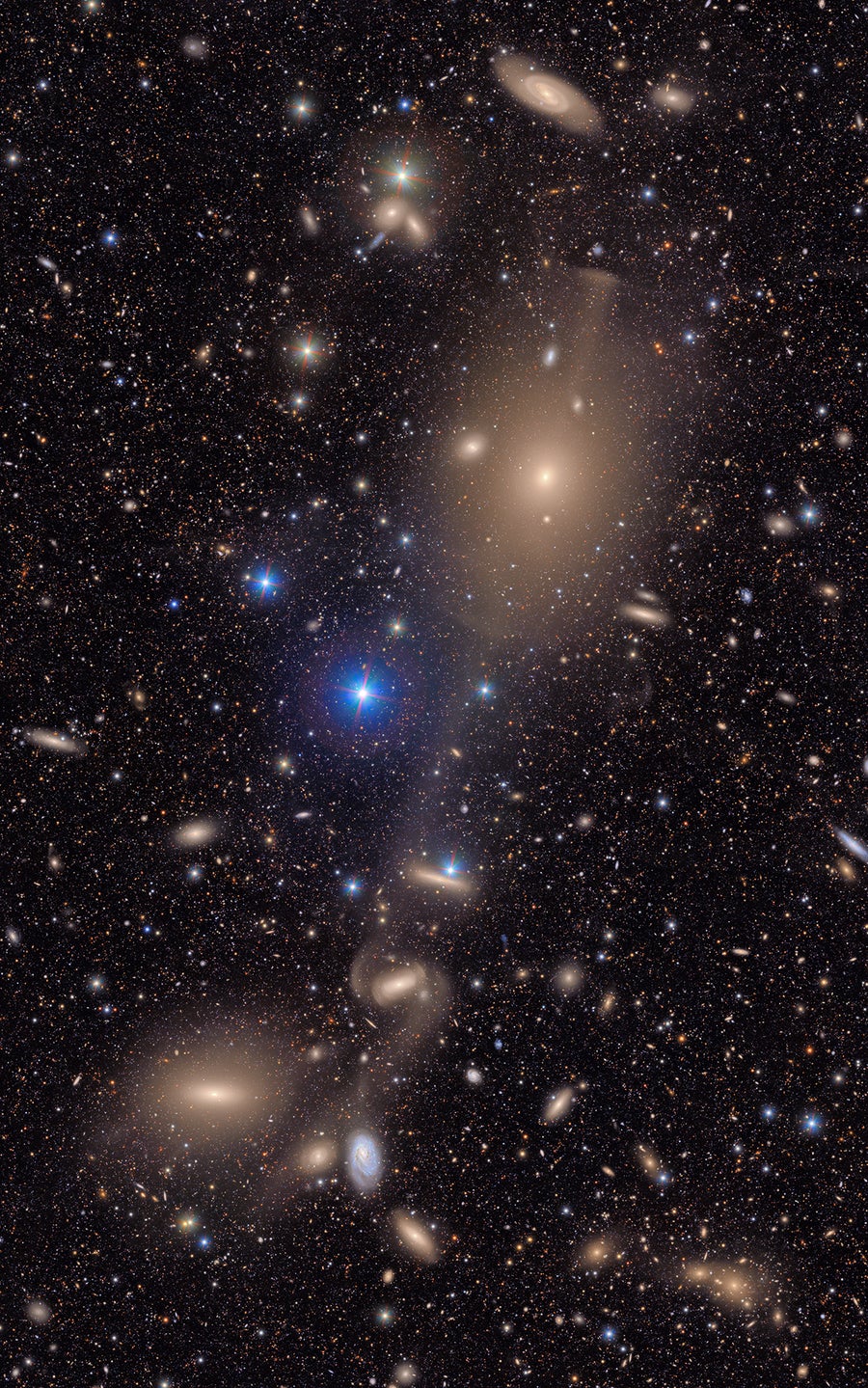

This image shows a small section of NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory’s total view of the Virgo cluster. Bright stars in the Milky Way galaxy shine in the foreground, and many distant galaxies are in the background.
NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory
The Rubin Observatory has promised to reveal additional imagery during the unveiling event later today, including the full video of the massive view of countless galaxies and another video depicting the more than 2,000 asteroids the telescope has already discovered in just 10 hours of observations.
These first glimpses from Rubin showcase the observatory’s unprecedented discovery power. The telescope will survey the entire southern sky about once every three days, creating movies of the cosmos in full color and jaw-dropping detail.
“We’ve been working on this for so many years now,” says Yusra AlSayyad, an astronomer at Princeton University and the Rubin Observatory’s deputy associate director for data management. “I can’t believe this moment has finally come.”











Leave a Reply