Sahara Dust Clouds Are Heading to Florida and Beyond
Clouds of dust blown off the Saharan Desert into the southeastern U.S. could affect local weather and make sunrises and sunsets particularly vivid
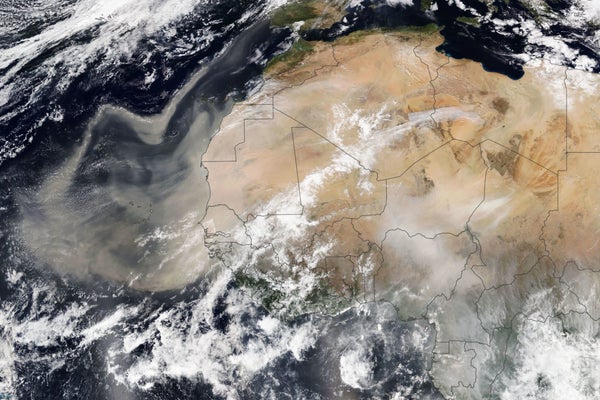

Each year, seasonal winds carry tens of millions of tons of Saharan dust across the Atlantic and beyond. On February 18, 2021, NOAA-20’s VIIRS captured a dramatic display of airborne dust.
NASA Earth Observatory image by Lauren Dauphin, using VIIRS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE, GIBS/Worldview, and the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership
Clouds of dust drifting from the Sahara Desert over the Atlantic Ocean could make for unusual-looking sunrises and sunsets, as well as potentially drier weather, over Florida and parts of the southeastern U.S. in the coming days.
What’s Happening
Between late spring and early fall, dust from the Saharan gets blown out over the Atlantic Ocean every three to five days. When conditions are right, air masses that are filled with this dust can make it across the thousands of miles required to reach North America. Meteorologists call this type of air mass the Saharan Air Layer, or SAL.
On supporting science journalism
If you’re enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Currently, on Friday, a thin SAL is dispersing over Florida, says Ana Torres-Vazquez, a meteorologist at the National Weather Service’s Miami office, who adds that this could interfere with some storms carried into the peninsula by a cold front on Saturday. Another layer of dust—this one thicker and denser—may then blow in next week, although that forecast is currently less certain, Torres-Vazquez notes.
It’s worth noting that the Atlantic hurricane season officially begins on June 1. In general, the SAL tends to dry the atmosphere it drifts through—so some scientists think these dust clouds may actually impede hurricane development. For now, however, forecasters aren’t expecting any tropical storms to develop in the Atlantic within the coming week.
Sunrise, Sunset
The effect that will be most noticeable to local residents as the dust lingers might be unusual sunrises and sunsets.
“When you have Saharan dust or any other kind of particulate, if the sun is coming in at an angle, like during sunrise or sunset,” Torres-Vazquez says, “it can hit those particulates that are close to the ground just right and result in those different, kind of orangey-reddish colors.”
Other parts of the country might also see enhanced sunrises and sunsets during the coming days from a different kind of particulate—wildfire smoke. Canada is experiencing yet another brutal year for wildfires, with nearly 700,000 hectares, or more than 2,500 square miles, burned to date.
Right now fires are particularly bad in the provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba, in part because of high temperatures stuck over central Canada. Smoke from these blazes is expected to reach U.S. states, including Minnesota, Wisconsin, Illinois and Michigan, in the coming days.
Depending on how close the dust and smoke get to Earth’s surface, these kinds of particulate matter can be harmful to people’s health, particularly for people who are very young or very old and those who have asthma or heart or lung disease. The Air Quality Index can help you gauge whether you should take any precautions.












Leave a Reply